
By 2030, as the global population is expected to reach 8.6 billion, the youth population will increase to more than 1.3 billion (UN DESA). Pervasive unemployment, underemployment and longer school- to-work transitions are some of the most significant challenges facing the rising youth population. These challenges are the result of the lack of adequate professional opportunities for young people, and increasingly skewed skills imbalances, i.e. shortages, surpluses and mismatch of skills acquired versus those demanded by the world of work.
To cope with evolving skills demands, technical and vocational education and training (TVET) systems are investing in new learning pathways, setting-up innovative initiatives and programmes, and developing new partnerships. Responsive skills development programmes need to ensure not only the functional consistency with the demands from the world of work, but also the development of transversal skills and competences that enable youth to respond to changing industry demands.
What Does TVET Offer for Youth Skills Development?
267 million young people (aged 15-24) are not in employment, education or training (NEET), and many more endure substandard working conditions (ILO 2020). In the wake of technological, environmental and demographic shifts, the challenge of creating jobs and livelihood opportunities is immense. However, creating job opportunities without responsive skills development of the youth for the world of work will exacerbate the skills mismatch and yield limited effects.
TVET systems around the world are currently in a state of transformation and innovation to better respond to current and emerging challenges. This transformation, though varied across regions and levels of development, includes the transition of TVET from a vehicle for functional skills development for employability to the development of broad-based and transversal skills that enable its graduates to access further opportunities for learning and upskilling throughout the course of their lives. As transversal skill demands continue to evolve, TVET provides a pathway for young people to develop their competences and transition to the world of work.
Mainstreaming Entrepreneurial Learning in TVET
Entrepreneurial learning offers a realistic and achievable means to develop the transferable skills that society and the labour market expect of today’s citizens. Recognizing the important role that entrepreneurship can play in countering the challenges of youth employment, UNESCO-UNEVOC has made a concerted effort to promote entrepreneurial learning across the TVET sector.
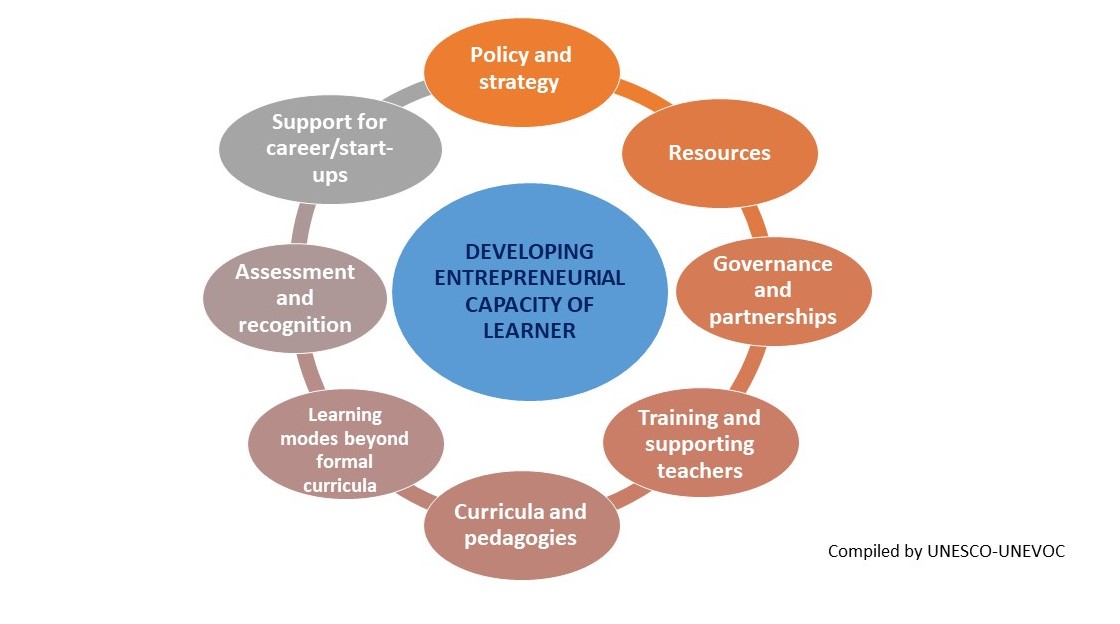
UNESCO-UNEVOC has been coordinating consultations on entrepreneurial learning in TVET with UNEVOC Centres and other experts from around the world. These consultations explored the current state of entrepreneurial learning in TVET policies and programmes, and facilitated the exchange of experiences, opportunities and challenges to mainstreaming entrepreneurial learning in TVET systems. In November 2018, UNESCO-UNEVOC organized a two-week virtual conference on ‘Entrepreneurial Learning in TVET’, which enabled TVET stakeholders from more than 83 countries to share their approaches and insights on the topic. The main findings were compiled in a virtual conference report and a selection of the practical cases have been included in a discussion paper.
Practical Guide on Entrepreneurial Learning
UNESCO-UNEVOC has developed a practical guide that aims to support TVET actors in mainstreaming entrepreneurial learning at the institutional level, taking into account different socio-economic contexts. The overall objective is to contribute to strengthening the capacity of the TVET sector to help prepare young people for the changing world of work and for personal development. The practical guide also provides a step-by-step Entrepreneurial Learning Institution Canvas (ELIC) that TVET administrators, managers and teaching staff can implement at their institutions to foster an 'entrepreneurial culture'. The ELIC tool allows TVET institutions to develop their own concept for entrepreneurial learning, map out which entrepreneurial learning activities are relevant to their institutional context and apply innovative approaches and models.
Access the interactive guide here.
Original article from UNESCO UNEVOC.


